Jointed Goatgrass
Information
Aegilops cylindrica - Poaceae Family




Identification
- Flowers: The plant produces red (when mature) or straw-colored spikes. Spikes are cylindrical and contain 2-12 spikelets per spike.
- Seeds: The spikelets are awned with the longest awns at the top of the spike. At maturity the seed heads break into individual segments. The plant spreads solely by seed.
- Leaves: The leaves are alternate, up to 0.5 inches wide with thin hairs along the margins. The connection to the plant stem is short and membranous.
- Flowering Time: May to June
- Life cycle: Jointed Goatgrass flowers in early to mid-June. Some jointed Goatgrass seeds germinate early and the remainder of the seeds may persist in the soil for years. Seeds usually germinate from early August - October but they can also germinate in late spring and still mature if temperatures are low enough.
Impacts
- Jointed Goatgrass readily invades wheat fields where, once established, it is extremely difficult to control.
- Jointed Goatgrass can hybridize with winter wheat, and an infestation can rapidly reduce crop yields by 30-50%.
- Sharp barbs can injure livestock, wildlife, and humans.
Control
Most effective control methods
- Because of its genetic similarity to winter wheat, Jointed Goatgrass is extremely difficult to control without damaging desirable plants, however, some selective herbicides can be effective. Follow advertised directions and warnings prior to herbicide use.
- Small infestations can be controlled through tilling or hand-pulling.
- There are currently no biological control agents available.
- Crop rotations can be effective in controlling Jointed Goatgrass.
Large Images
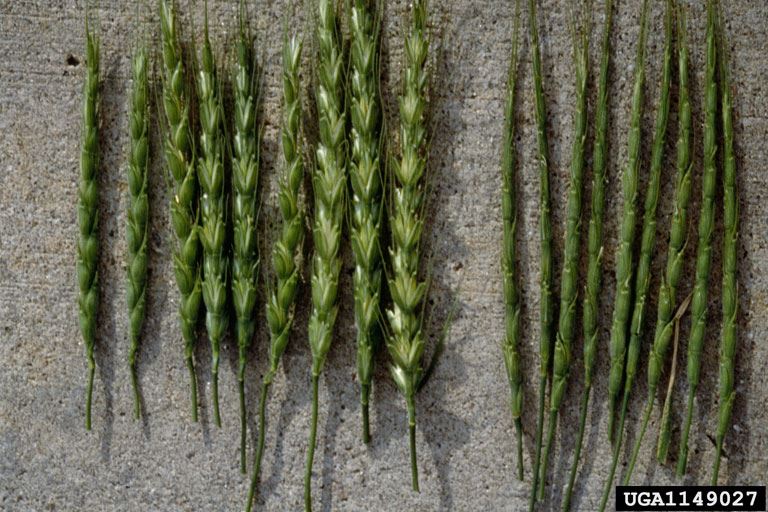

Jointed goatgrass compared to wheat. Wheat is pictured on the left, jointed goatgrass is on the right.

Jointed goatgrass: flowers
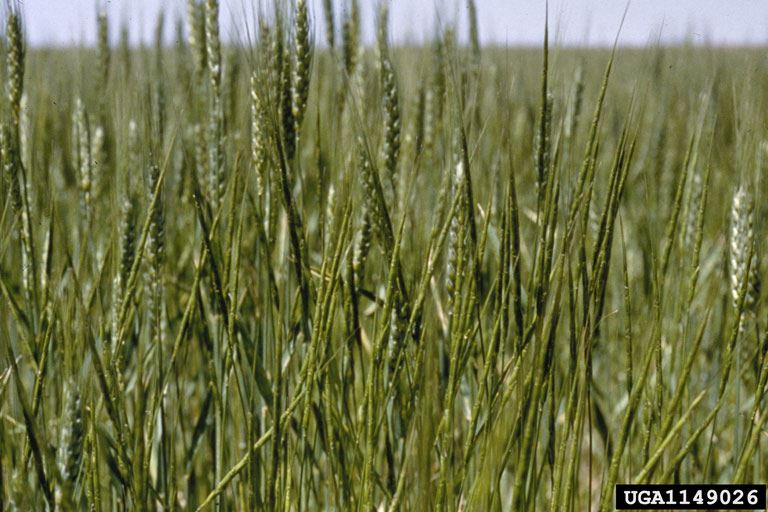

Jointed goatgrass: infestation
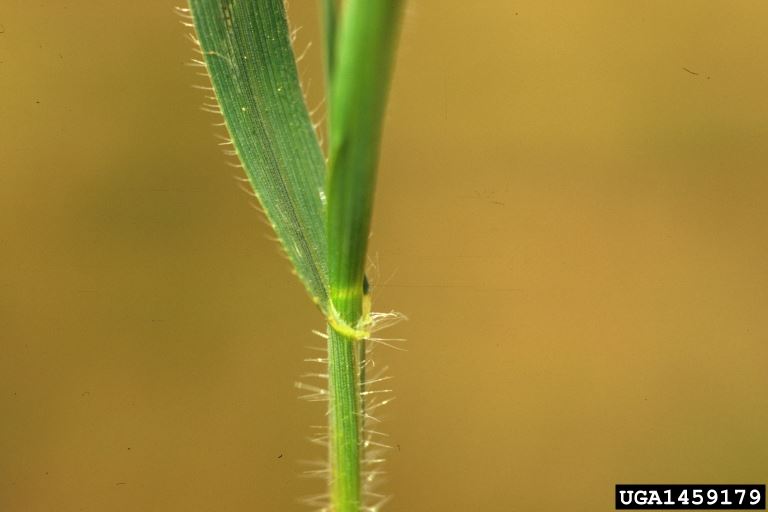

Jointed goatgrass: stem and foliage

Jointed goatgrass: seedlings
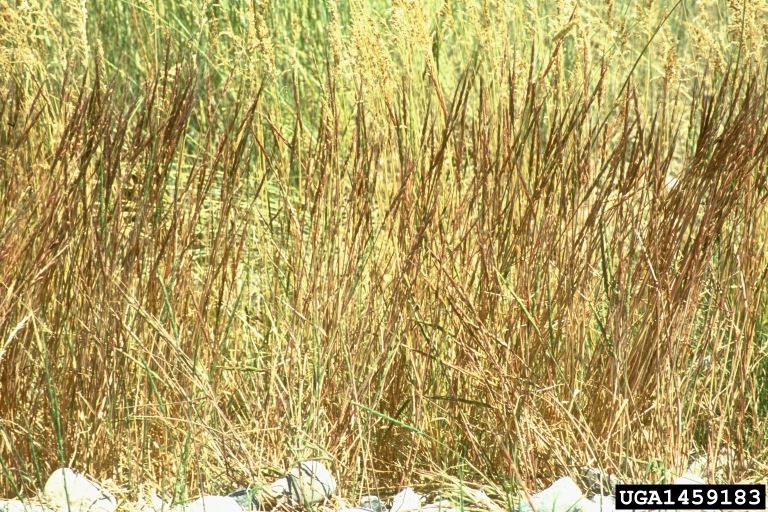

Jointed goatgrass: infestation
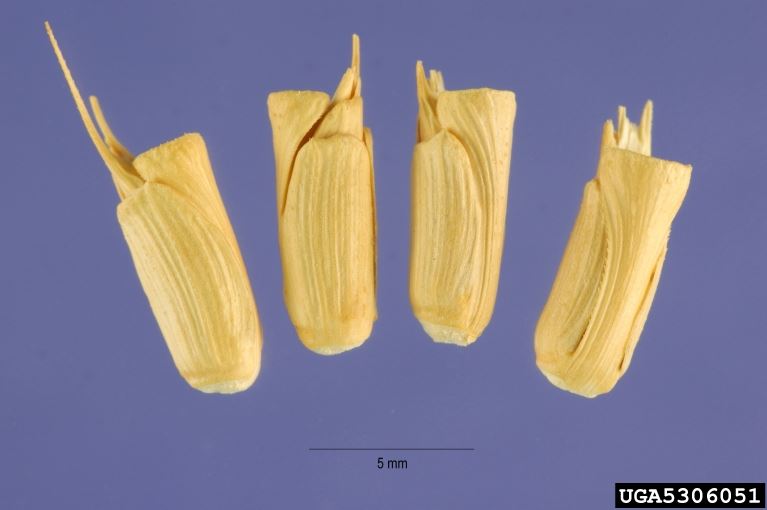

Jointed goatgrass: seeds
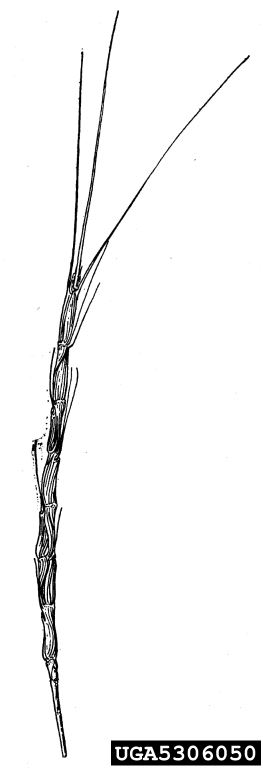
Jointed goatgrass
Resources
-
References
DiTomaso, J.M., G.B. Kyser et al. (2013). Weed Control in Natural Areas in the Western United States [PDF file]. Weed Research and Information Center, University of California. Retrieved from https://wric.ucdavis.edu/information/natural-areas/wr_A/Aegilops_cylindrica-triuncialis.pdf View PDF
Lyon, D., & Klein, R. (2007, July). Controlling jointed goatgrass [PDF file]. Retrieved from https://weedscience.unl.edu/extensionPublications/nebguides/g1252.pdf View PDF
United States Department of Agriculture. (2014, September). Field guide for managing jointed goatgrass in the southwest [PDF file]. Retrieved from https://www.fs.usda.gov/Internet/FSE_DOCUMENTS/stelprdb5410115.pdf View PDF
University of Arizona Cooperative Extension. A northern Arizona homeowner’s guide to identifying and managing invasive plants. Retrieved from https://www.nazinvasiveplants.org/jointed-goatgrass/
Washington State Noxious Weed Control Board. Jointed Goatgrass. Retrieved from https://www.nwcb.wa.gov/weeds/jointed-goatgrass
Washington State University. (2016, August). Jointed goatgrass: best management practices central great plains [PDF file]. Retrieved from http://cru.cahe.wsu.edu/CEPublications/eb2033e/eb2033e.pdf View PDF




