Yellow Toadflax
Information
Linaria vulgaris - Scrophulariaceae Family - Creeping perennial




Identification
- Flowers: Yellow snapdragon-like flowers with orange throats, crowded at the top of the stem.
- Seeds: Black to brown seeds with a papery wing, held in a capsule. Yellow toadflax can reproduce by seeds and by its horizontal rootstalks which send up new shoots.
- Leaves: Light green linear leaves arranged alternately along the stem. Unpleasant smell.
- Flowering Time: June - September
- Life cycle: Perennial that grows 8 to 31 inches tall from creeping roots, often forming colonies.
Impacts
- Invades roadsides, edges of fields, rangelands, meadows, cultivated fields and wastelands.
- Yellow toadflax competes with desirable plants and reduces their yield. It is seldom eaten by livestock.
Control
Most effective control methods
- Overall, all toadflax species are difficult to control and management plans should integrate as many strategies as possible to increase potential for success.
- For small infestations, or single plants, digging and monitoring for new plants is imperative.
- For larger infestations, chemical applications using the herbicides Tordon 22K, Picloram, or Telar, have shown to have higher levels of success when applied to the flowering stage over multiple years. Yellow toadflax usually recovers from single applications.
- Several classical biocontrol agents are available to use against toadflaxes, including a flower-feeding beetle and seed capsule weevil. Unfortunately, an ideal yellow toadflax biological control agent has yet to be identified; the approved agents discussed above can contribute to the overall erosion of the weed’s fitness, and therefore merit consideration when an integrated weed management approach is adopted against this species.
Control methods and timing
| March | April | May | June | July | Aug | Sept | Oct |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Prev Mech |
Prev Mech |
Prev Mech |
Prev Mech Chem |
Prev Mech Chem |
Prev Mech |
Prev Mech |
Prevention (Prev) Monitor and destroy new plants before seed production.
Mechanical (Mech) Hand pulling, digging, cutting, mowing and tilling.
Cultural (Cult) Biological control agents, livestock grazing, and revegetation practices.
Chemical (Chem) Selective herbicides based on the plant and the specific location. Check our weed fact sheets for specific control information.
Large Images

Yellow toadflax in bloom

Yellow toadflax foliage, looking straight down on the plant
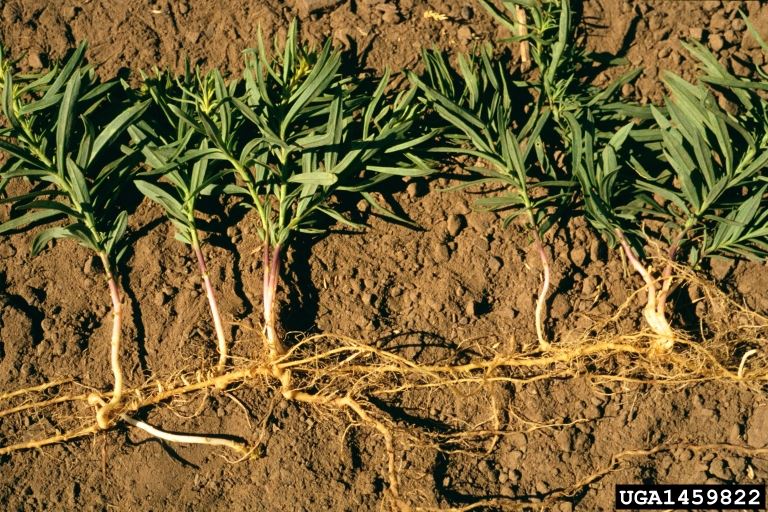

Yellow toadflax: roots

Yellow toadflax: infestation
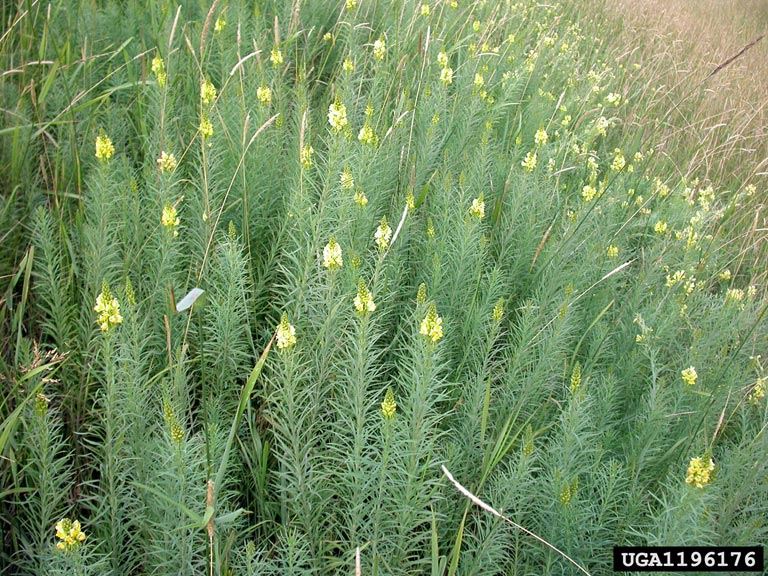

Yellow toadflax: infestation
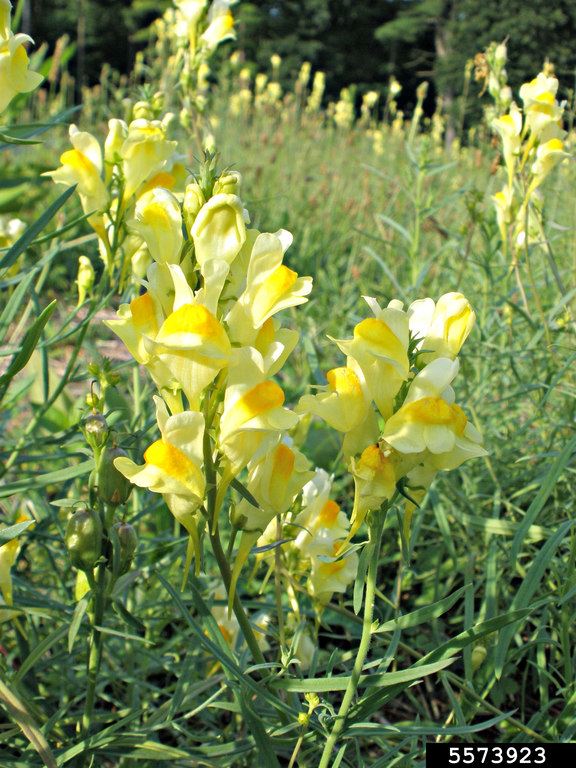

Yellow toadflax: flowers
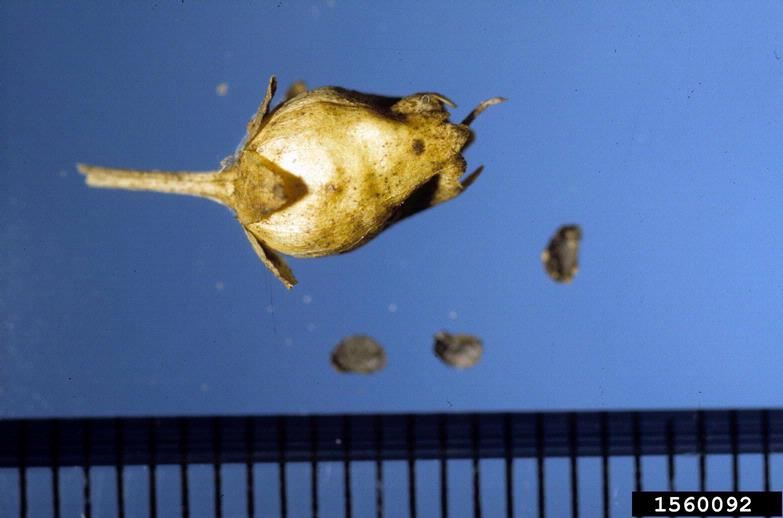
Yellow toadflax: seeds
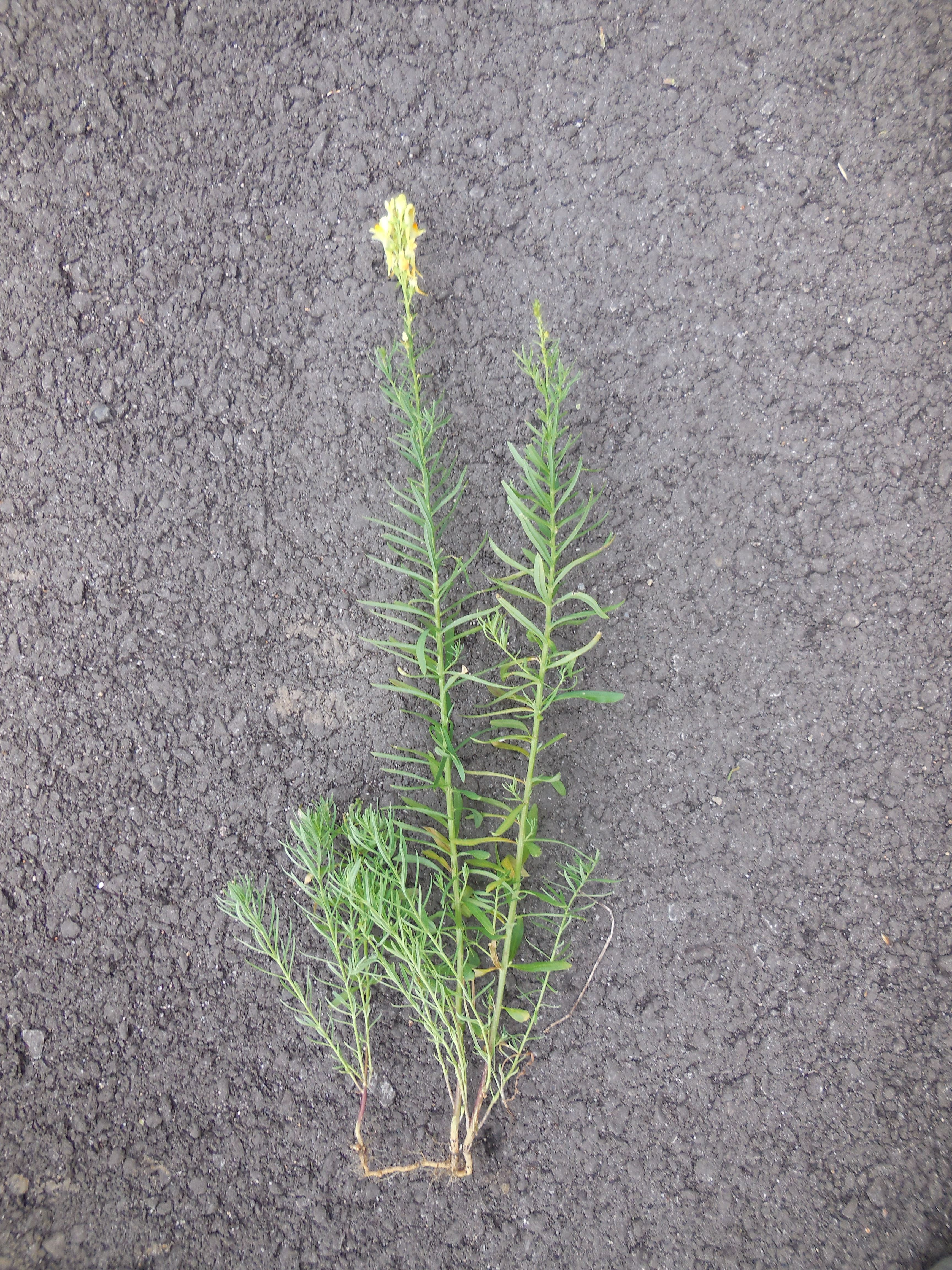

Yellow toadflax: stems, foliage, flowers, and roots
Resources
-
Links
-
- University of Nevada Cooperative Extension View PDF
-
References
Beck, K.G. (2014, December). Biology and management of the toadflaxes [PDF file]. Retrieved from https://extension.colostate.edu/docs/pubs/natres/03114.pdf View PDF
DiTomaso, J.M., G.B. Kyser et al. (2013). Weed Control in Natural Areas in the Western United States [PDF file]. Weed Research and Information Center, University of California. Retrieved from https://wric.ucdavis.edu/information/natural-areas/wr_L/Linaria_vulgaris.pdf View PDF
Jacobs, J. & Sing, S. (2006, November). Ecology and management of yellow toadflax [PDF file]. Retrieved from https://www.fs.fed.us/rm/pubs_other/rmrs_2006_jacobs_j001.pdf View PDF
Rocky Mountain Biological Laboratory. Yellow toadflax. Retrieved from http://www.rmbl.org/yellow-toadflax/
United States Department of Agriculture. (2014, September). Field Guide for Managing Dalmation and Yellow Toadflaxes in the Southwest [PDF file]. Retrieved from https://www.fs.usda.gov/Internet/FSE_DOCUMENTS/stelprdb5410111.pdf View PDF




